How Long Does THCA Flower Stay in Your System?
Detection Times for THCA: What You Need to Know
THCA, once decarboxylated, can be detected in drug screenings, but detection windows vary depending on the test used.
- Breath Analyzers: Detect THCA use within a short window of up to three hours after consumption.
- Hair Follicle Tests: Provide the longest detection window, capable of identifying THCA use up to 90 days later.
Understand these detection timelines is crucial for making informed decisions regarding THCA use.

Understanding THCA and Drug Testing: What You Need to Know
Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) is the precursor to Delta-9 THC, the compound associated with the psychoactive effects of cannabis. Unlike Delta-9 THC, THCA is non-intoxicating and typically does not trigger a positive result on a marijuana drug test.
However, it’s important to understand how THCA behaves in the body, particularly if you are subject to scheduled or random drug screenings. When THCA is exposed to heat—such as during vaping or smoking—it undergoes decarboxylation, converting into THC. This process increases the likelihood of testing positive for THC in drug screenings.
This guide breaks down the average time decarboxylated THCA remains detectable in various types of samples, providing you with all the information needed to approach drug tests with confidence.
Detection Windows Vary by Screening Method:
- Urine Tests: Detect decarboxylated THCA for up to 30 days.
- Blood Tests: Provide the shortest detection period, at just 24 hours.
THCA is Non-Psychotropic:
THCA does not produce intoxicating effects and is not directly targeted in standard drug screenings. However, when heated (through vaping or smoking), it converts into THC, increasing the likelihood of a positive marijuana drug test.Raw THCA Consumption is Safe:
Digestion and metabolism alone cannot convert THCA into THC. Eating raw THCA should not result in a positive drug test unless you’ve also smoked or vaped it.
Understanding these distinctions can help you navigate drug screenings with greater confidence.

Does THCA Show Up on Drug Tests? What You Need to Know
It’s crucial to understand that THCA, on its own, is not typically detected in standard drug screenings. Unlike THC, THCA is neither illegal nor listed as a substance of concern in most testing protocols.
The Risk of Failing a Drug Test
The primary risk comes from vaping or smoking THCA products. When exposed to heat, THCA undergoes decarboxylation, converting into THC—the compound responsible for positive marijuana test results.
Clearance Time for THCA
The body may take approximately 45 days to fully clear THCA. However, this timeline can vary based on several factors:
- Age: Metabolism slows with age, potentially lengthening clearance times.
- Metabolic Rate: Individuals with higher metabolism may process THCA more quickly.
- Dosage and Frequency: Larger or more frequent doses of THCA can extend detection times.
In the next section, we’ll explore how these factors influence detection and clearance, helping you better understand what to expect.

Understanding THCA and Drug Screenings
Most drug screenings are designed to detect THC metabolites, not THCA. This means that THCA, in its unheated and non-intoxicating form, is unlikely to trigger a positive result on standard drug tests.
What Makes THCA Different From THC?
THCA is a non-psychotropic compound, meaning it doesn’t produce the mind-altering effects associated with THC. Found in raw cannabis, THCA is believed to have therapeutic potential, but it remains inactive until heated.
Decarboxylation: The Key Process
THCA becomes THC when exposed to heat in a process known as decarboxylation. This process activates the cannabinoids, making them effective for recreational and medicinal purposes.
Detection of Decarboxylated THCA
Once decarboxylated, THCA converts to THC and can then be detected using standard drug testing methods, including:
- Urine Tests
- Saliva Tests
- Blood Tests
- Hair Follicle Tests
Raw THCA and Drug Tests
In rare cases, advanced testing may detect raw THCA. This is more common when THCA is consumed in raw or edible forms. However, consuming raw THCA can lead to unpleasant side effects, such as:
- Nausea
- Stomach upset
- Skin rashes
- Respiratory issues
Understanding how THCA interacts with the body and drug tests can help you make informed decisions about its use and potential impacts.
THCA Metabolism Process: How Does the Body Absorb and Flush THCA?
The way the body absorbs and metabolizes THCA depends heavily on the method of consumption. Whether vaped, smoked, ingested, or applied topically, each approach has unique pathways and impacts on how the compound is processed and eventually eliminated.
The Journey of THCA Through Different Consumption Methods
1. Smoking or Vaping THCA
- Absorption: When THCA is smoked or vaped, the compound undergoes decarboxylation, converting into THC upon exposure to heat. The lungs rapidly absorb the resulting THC, which enters the bloodstream and travels to the brain.
- Metabolism: The liver processes the THC into metabolites, primarily 11-hydroxy-THC and THC-COOH, which are stored in fat tissues.
- Elimination: These metabolites are slowly excreted through urine and feces over days or weeks, depending on factors like frequency of use and body fat percentage.
2. Ingesting THCA (Edibles)
- Absorption: THCA consumed in raw or edible form bypasses decarboxylation and enters the digestive system as-is.
- Metabolism: In its raw form, THCA is not converted into THC during digestion, meaning it doesn’t produce intoxicating effects. The liver processes the compound, and any unused THCA is excreted.
- Elimination: THCA is flushed out of the body more quickly when consumed raw, as it doesn’t bind to fat cells like THC metabolites.
3. Topical Application
- Absorption: When applied to the skin, THCA is absorbed locally and does not enter the bloodstream in significant amounts.
- Metabolism: The compound remains localized, interacting with cannabinoid receptors in the skin, providing potential therapeutic effects without systemic absorption.
- Elimination: The body metabolizes the compound at the site of application, with minimal systemic waste to excrete.
Factors Influencing THCA Metabolism
- Method of Consumption: Smoking and vaping introduce decarboxylated THCA (as THC) directly into the bloodstream, while raw consumption avoids conversion.
- Frequency of Use: Regular users may experience slower elimination rates due to the accumulation of metabolites in fat tissues.
- Body Composition: Higher body fat percentage can result in longer detection windows for decarboxylated THCA metabolites.
- Metabolic Rate: Faster metabolisms can process and eliminate THCA and its metabolites more efficiently.
By understanding the journey of THCA through the body, you can make informed decisions about your preferred consumption method and its potential impacts.
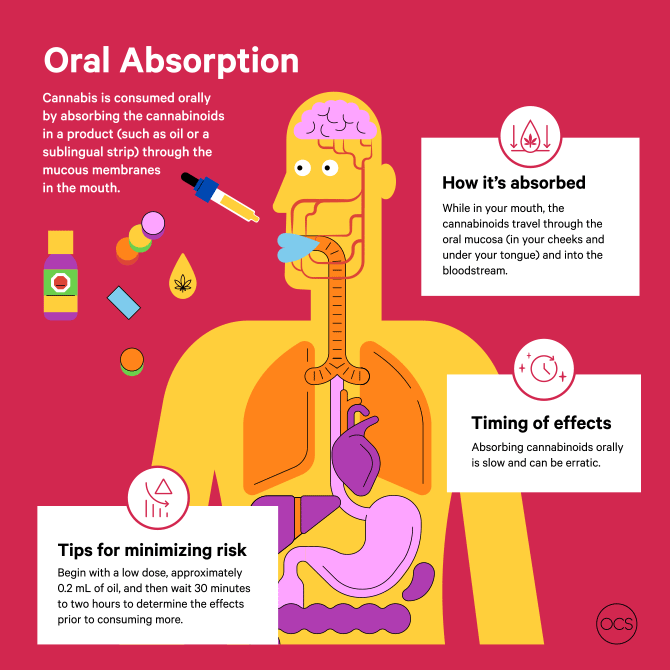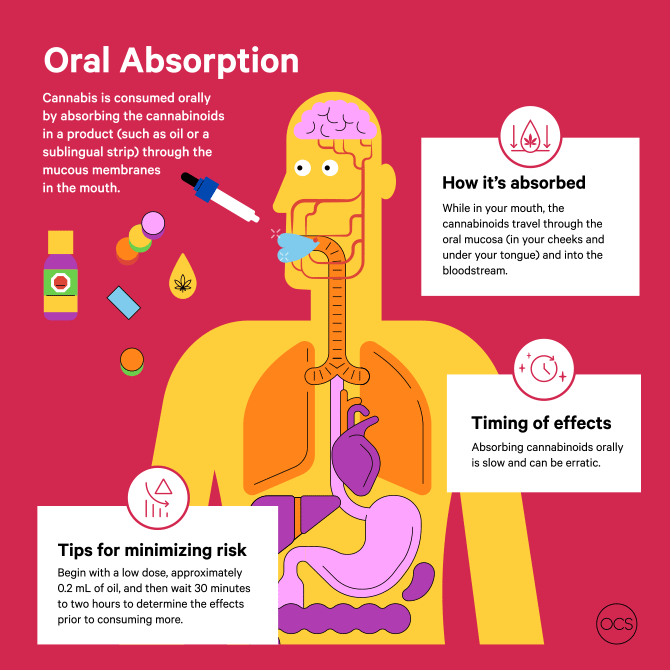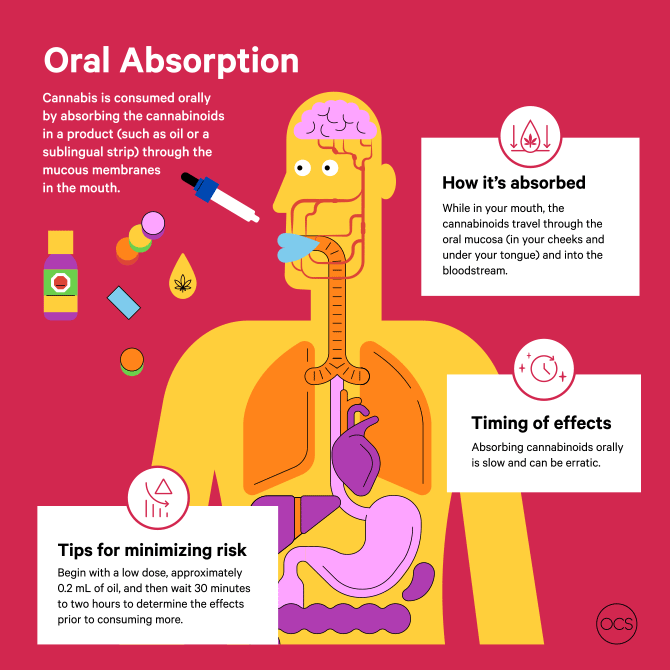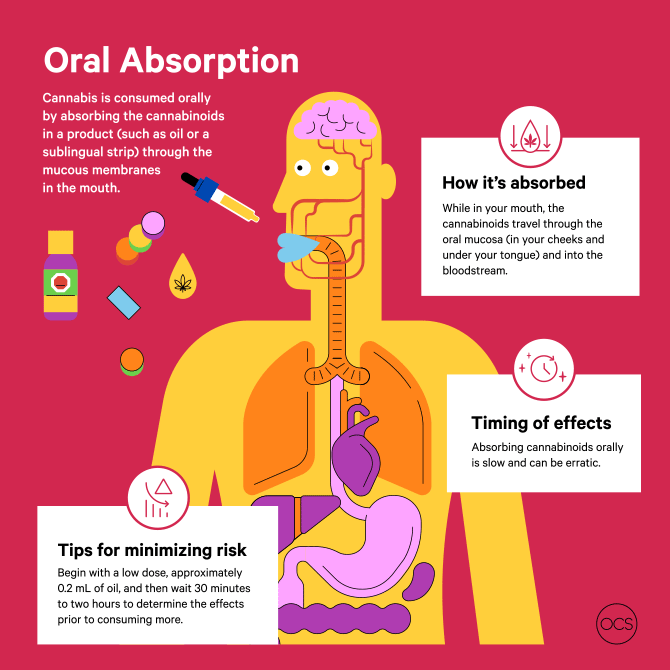
The Three Phases of THCA Metabolism
Phase 1: Oral Absorption
When THCA is consumed orally—via gummies, raw juices, or other edibles—it undergoes digestion in the stomach and intestines. From there, it moves to the liver for processing. Unlike decarboxylated THC, raw THCA is not fully absorbed into the bloodstream during this phase, limiting its systemic effects.
Phase 2: Metabolic Process
In the liver, enzymes metabolize THCA, transforming it into water-soluble forms. This allows the compound to be prepared for excretion. Importantly, the chemical structure of THCA remains largely intact, preventing it from converting into THC unless exposed to heat beforehand.
Phase 3: Excretion
The majority of THCA bypasses systemic circulation and heads directly to the kidneys and digestive tract for elimination. Only a small portion may enter the bloodstream temporarily before being flushed out. This limited absorption contributes to THCA’s non-intoxicating properties when consumed raw.
Understanding these phases highlights why consuming raw THCA differs significantly from consuming decarboxylated THC products in terms of both effects and metabolism.
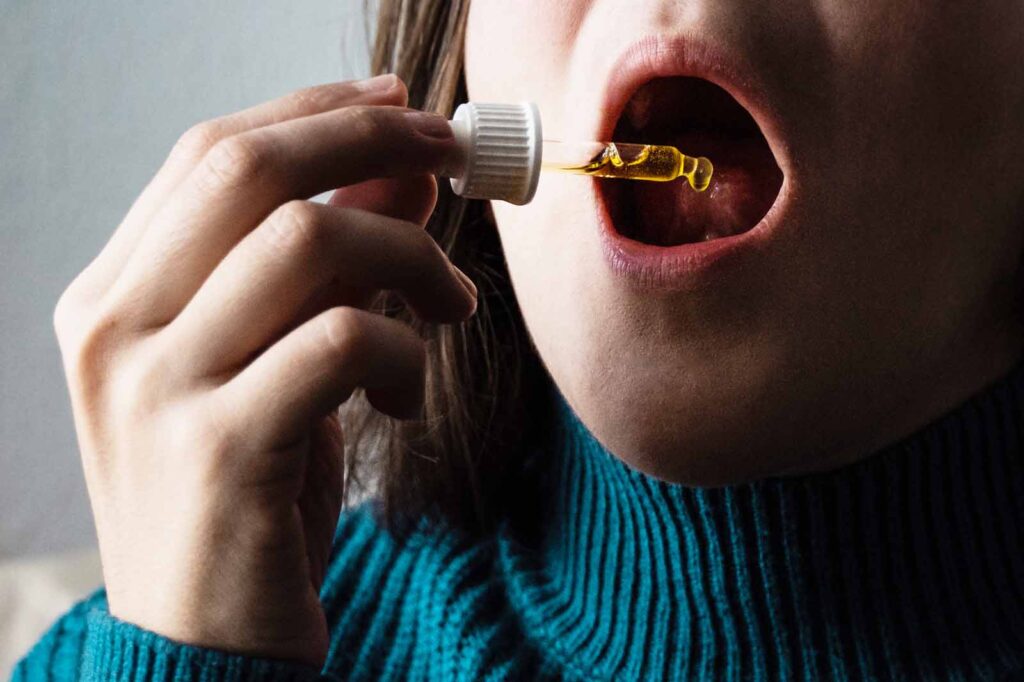

Metabolism of THCA: Sublingual Route
Phase 1: Absorption
Sublingual consumption, such as tinctures or oils placed under the tongue, takes a direct route into the bloodstream. THCA is absorbed through the thin mucosal tissue under the tongue, bypassing the digestive system entirely. This method enhances bioavailability, allowing a greater concentration of THCA to enter the bloodstream compared to oral consumption.
Phase 2: Partial Metabolism
Once circulating in the bloodstream, THCA reaches the liver for partial metabolism. Here, enzymes break it down into forms that are easier for the body to process and eventually eliminate.
Phase 3: Excretion
After metabolism in the liver, THCA is excreted primarily in bile, which passes through the digestive system and exits as feces. A smaller portion may be eliminated through urine, but fecal excretion is the predominant pathway.
This sublingual method ensures faster absorption and higher bioavailability compared to traditional oral ingestion, making it an efficient way to consume THCA without undergoing extensive digestive processing.

Metabolism of THCA: The Inhalation Route
Phase 1: Inhalation
When consumed by inhalation, such as through tinctures or oils dropped under the tongue, THCA bypasses the digestive system. The compound is absorbed directly into the bloodstream through the thin mucosal tissue under the tongue. This direct absorption improves its bioavailability, allowing a higher concentration of THCA to enter the bloodstream compared to other consumption methods.
Phase 2: Partial Metabolism
After entering the bloodstream, THCA is processed by the liver. During this phase, the liver begins to partially metabolize THCA, converting it into water-soluble forms that are easier for the body to process and eliminate.
Phase 3: Excretion
Once metabolized by the liver, THCA is primarily excreted through bile and exits the body via the feces. A smaller portion may be eliminated through urine, but the majority of THCA is excreted as feces.
This sublingual method offers an efficient route for THCA absorption, improving bioavailability and leading to faster effects due to its direct entry into the bloodstream.
What Factors Influence the Detection Window of Decarboxylated THCA in Your Body?
Several factors play a role in determining how long altered THCA stays in your system, including metabolic rate, age, and frequency of use.
Metabolic Rate and Age: As we age, our metabolism naturally slows down, which affects how quickly substances are processed and expelled from the body.
Frequency of Use: The more often THCA is consumed, the longer it will take for the body to eliminate it. Those who use THCA more frequently tend to have a longer detection window, while occasional users can process and expel the compound more quickly.
- One-time users: Generally, these individuals can expect to clear THCA from their system in about 3 to 5 days.
- Moderate users: For those consuming up to four times a week, the detection window is typically around 7 days.
- Chronic users: Individuals who use THCA daily might take 15 days or more to fully expel the compound.
- Heavy users: In some cases, those with frequent, high doses may need 30 to 45 days for the body to eliminate THCA completely.
Understanding these factors can help you gauge how long THCA might stay in your system, particularly if you’re preparing for a drug test.
How Long Does THCA Stay in Your Hair?
Hair follicle drug tests are more comprehensive than urine tests, offering a deeper look into a person’s substance use history. While less invasive, they can reveal a longer history of usage, providing a broader timeline of substance consumption.
The process involves collecting hair samples, typically from the back of the head near the neck, with strands taken closest to the scalp to give the most recent information.
These tests are commonly required for jobs with high injury risks, such as construction, or in legal situations like probation, child custody, or domestic violence cases. Hair follicle tests can detect substance use for up to three months, offering a more extended detection window than other tests.
As for their accuracy, a 2015 study found that hair follicle tests can identify more than 52% of recent cannabis use, which also gives an indication of the presence of THCA in the body, though it may not be as precise as other methods in identifying THCA specifically.
How Long Does THCA Stay in Your Spit?
Fast Answer: 24 to 48 Hours
Saliva drug screenings share similarities with COVID-19 swab tests, involving the collection of oral samples using a sponge or absorbent pad. The tester swabs the inside of the individual’s cheek to gather the sample, making this method quick and non-invasive.
The entire process takes about three minutes, with results typically available within 24 hours. To ensure accurate readings, individuals are required to avoid eating or drinking for at least ten minutes before the test.
When it comes to detecting cannabis compounds, saliva tests have a relatively short detection window, usually up to 24 hours. However, studies indicate that inhaled THC can sometimes be detected for as long as 30 hours, while ingested cannabis compounds may remain traceable in saliva for up to 48 hours.
.
How Long Does THCA Stay in Your Blood?
Fast Answer: 2 To 24 Hours
If you’re uneasy about needles, blood drug screenings might feel invasive and unpleasant. However, in situations requiring detailed insights into recent substance use, this method is sometimes necessary.
Employers may mandate blood tests to investigate erratic employee behavior or as part of monitoring after rehabilitation. These tests provide precise results but are less commonly used due to their invasiveness and limited detection window.
Blood screenings have the shortest detection window among drug testing methods, ranging from 2 to 24 hours. Due to this brief timeframe, most organizations favor alternative testing methods for broader substance use detection.
Can a Breath Test Detect THCA

Breathalyzers and cannabis detection is not a straightforward topic; it depends significantly on the type of device used.
Currently, standard breathalyzers are designed to detect alcohol and cannot identify other substances like THC. If law enforcement needs to determine THC presence, alternative methods, such as saliva tests, are typically used. Additionally, there is no chemical test available that can measure cannabis impairment similarly to how alcohol is assessed through breathalyzers.
However, emerging breathalyzer technologies are being developed to detect THC molecules in a person’s breath. These advanced devices can isolate active THC particles, offering a potential new method for cannabis detection.
The key limitation lies in timing. THC particles are only detectable in breath for a short window—usually within two to three hours after inhalation. Therefore, immediate testing is critical for accurate results.
In summary, while breathalyzers can detect cannabis use under specific conditions, factors like device capability and timing are essential considerations.
Why Is Unheated THCA Flower Typically Undetected?
Unheated THCA is the raw, non-psychoactive form of the compound and is generally not detected in standard drug screenings. It only converts into THC, the psychoactive substance, when exposed to heat, such as through smoking or vaping, which is when it might show up on a drug test.
However, this does not make unheated THCA completely undetectable. As previously mentioned, certain tests that identify cannabis metabolites could potentially pick up traces of THCA in the system. Additionally, specialized testing methods may also detect the presence of unheated THCA.
How Long Does It Take THCA to Leave Your System?
As discussed earlier, several factors influence how long THCA and THC remain in the body, including metabolic rate, age, exercise habits, and cannabis consumption frequency.
Since THC is fat-soluble, it binds to fat cells in the body. Individuals with higher physical activity levels and lower body fat may process and eliminate these compounds more efficiently. Conversely, those who exercise less or have higher body fat may retain these compounds longer.
In general, detection times vary:
- For infrequent users, THC can clear in three to seven days.
- For heavy, regular users, it can remain detectable for up to 30 days in urine tests.
These timelines provide a general estimate, but individual results may vary based on personal physiology and habits.
Does THCA Stay in Your System as Long as THC?
Because THCA is neither illegal nor a substance of significant concern, research on its exact retention time in the body is limited compared to THC. However, some evidence suggests that THCA may be expelled more quickly due to its non-psychotropic properties.
THCA does not linger in bodily systems—such as urine, blood, hair, or saliva—for extended periods. If your consumption is primarily THCA rather than THC, the likelihood of it affecting a drug screening is minimal, offering peace of mind for most users.
How Do You Get THCA Out of Your System Fast?
You generally don’t need to worry about THCA since standard drug tests don’t detect it. However, if THC is the concern, here’s the truth: there’s no guaranteed method to flush it out of your system to pass a drug test.
Common “detox” methods like drinking excessive water, consuming cranberry juice, or using detox teas and kits are ineffective. THC and its metabolites are eliminated naturally through the body’s metabolism, and no shortcuts can expedite this process significantly.
The most reliable way to clear THC from your system is to reduce or cease consumption. For casual users, THC metabolites typically remain in the body for about three to seven days. To minimize detection risk, keep your doses low, such as 2.5 to 5 milligrams weekly, and allow sufficient time for the substance to leave your system naturally.
What Contributes to False Positive THCA Tests?
Inhaling secondhand cannabis smoke does not typically result in a positive drug test. Research indicates that passive inhalation is “highly unlikely” to cause a failed screening, especially when using the standard threshold of 50 nanograms per milliliter of THC in initial tests.
However, certain hemp-based food products, such as oils or seeds, might cause a false positive. Additionally, medications like synthetic THC drugs (e.g., dronabinol), prescribed to stimulate appetite in conditions such as AIDS, can lead to the presence of cannabinoid metabolites in the system.
If you’re scheduled for a drug test, it’s wise to disclose any supplements or therapeutic medications you use to avoid misunderstandings in the results.
Conclusion
Currently, THCA is not included in the standard list of substances screened during drug tests. However, once THCA undergoes combustion, it converts into THC, which can then be detected. Understanding detection windows and testing methods is crucial to avoid a failed test that might lead to complications.
Before concluding, let’s address some of the most frequently asked questions.
FAQs About THCA and Drug Testing
Can THCA show up on a standard drug test?
No, THCA is typically not detected on standard drug tests. However, if THCA is combusted and converted to THC, it can become detectable in screenings.
How long does THC stay in the body after consuming combusted THCA?
The detection window for THC depends on factors like frequency of use, dosage, metabolism, and body composition. For casual users, THC may stay in the system for 3–7 days, while chronic users may retain it for up to 30–45 days.
Does consuming raw THCA trigger a positive drug test?
Consuming raw THCA is unlikely to result in a positive drug test, as it does not undergo combustion and remains in its non-psychotropic form. However, specialized tests that detect cannabis metabolites might identify its presence.
Can secondhand cannabis smoke cause a positive drug test?
Failing a drug test from secondhand smoke is highly unlikely, as passive inhalation typically doesn’t result in THC levels exceeding the standard 50 ng/mL threshold used in initial screenings.
Do detox methods like teas or cranberry juice help pass a drug test?
No, there is no scientific evidence to support that detox teas, cranberry juice, or other similar methods effectively remove THC or its metabolites from the body. The best approach is abstinence and allowing time for the body to naturally process and eliminate the compounds.
Can consuming hemp products lead to a false positive on a drug test?
Yes, certain hemp-derived products like oils or seeds may contain trace amounts of THC, potentially leading to a false positive result. It’s important to disclose any hemp-based supplements or medications you use before undergoing a drug test.





